5.3. User account templates#
User account templates in Nubus provide a powerful framework for standardizing user account creation across different organizational roles and purposes. This page targets functional administrators who manage and create user accounts for various purposes. This page describes how to define user account templates through the LDAP directory management module. The page explores the full range of available user attributes. It demonstrates syntax functions including case conversion, character filtering, and sub-string extraction. These features help you create dynamic, reusable templates that you use during user creation in Users module. This page has the following sections:
To manage user account templates, you need to open the LDAP directory management module. You find the module in the Domain section in the Management UI.
To select a template during user creation, you need to have at least one template defined. Fig. 5.3 shows where you select the user account template during user creation.
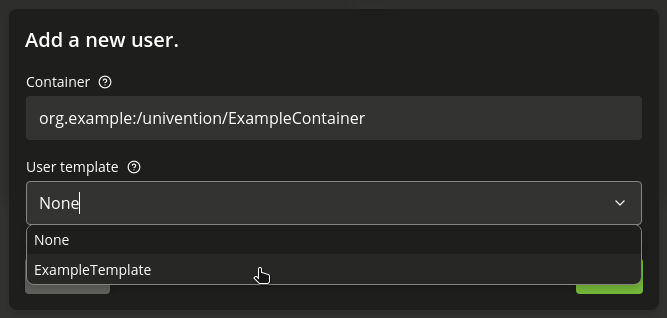
Fig. 5.3 Select a user account template during user account creation#
5.3.1. Create a user account template#
To create a user account template, use the following steps:
Open the LDAP directory management module.
Navigate to in the container structure on the left side and select
templates.To create a user template, click Add and select the object type
Settings: User template
5.3.2. Available user account attributes#
This section lists the user account attributes that are available by default in Nubus.
Depending on your environment and on additional components, your environment may offer additional user account attributes. You also find a description about how to retrieve the list for your environment.
List of available attributes, independent of installation
In a default installation of Nubus, independent of the installation target, such as Kubernetes or UCS, the user account has the attributes as shown in Listing 5.1. For a description of the respective attributes, see Users module.
Additional components may add more attributes. To retrieve the complete list of attributes, see the following instructions for your respective installation.
users/user variables:
General:
User account
title
firstname
lastname
username
description
overridePWHistory
overridePWLength
mailPrimaryAddress
Personal information
displayName
birthday
jpegPhoto
Organisation
organisation
employeeNumber
employeeType
secretary
Groups:
Primary group
primaryGroup
Additional groups
groups
Account:
Deactivation
disabled
userexpiry
Locked login
pwdChangeNextLogin
passwordexpiry
unlock
unlockTime
Activation
accountActivationDate
Windows
homedrive
sambahome
scriptpath
profilepath
sambaRID
sambaPrivileges
sambaLogonHours
sambaUserWorkstations
POSIX (Linux/UNIX)
unixhome
shell
uidNumber
gidNumber
homeShare
homeSharePath
Mail:
Advanced settings
mailAlternativeAddress
mailHomeServer
Mail forwarding
mailForwardCopyToSelf
mailForwardAddress
Contact:
Business
e-mail
phone
roomNumber
departmentNumber
street
postcode
city
state
country
Private
homeTelephoneNumber
mobileTelephoneNumber
pagerTelephoneNumber
homePostalAddress
Apps:
UMC preferences:
UMC preferences
umcProperty
Certificate:
General
userCertificate
Subject
certificateSubjectCommonName
certificateSubjectMail
certificateSubjectOrganisation
certificateSubjectOrganisationalUnit
certificateSubjectLocation
certificateSubjectState
certificateSubjectCountry
Issuer
certificateIssuerCommonName
certificateIssuerMail
certificateIssuerOrganisation
certificateIssuerOrganisationalUnit
certificateIssuerLocation
certificateIssuerState
certificateIssuerCountry
Validity
certificateDateNotBefore
certificateDateNotAfter
Misc
certificateVersion
certificateSerial
Guardian:
guardianRoles
guardianInheritedRoles
Password recovery:
DeregistrationTimestamp
DeregisteredThroughSelfService
RegisteredThroughSelfService
PasswordRecoveryEmailVerified
PasswordRecoveryMobile
PasswordRecoveryEmail
How to retrieve list of available attributes
The following steps describe how to retrieve the list of user account attributes available in your environment and depending on your installation.
Open a shell on a Nubus for UCS system
and run the command in
Listing 5.2.
Have a look at the output starting with users/user variables.
$ univention-director-manager users/user
To retrieve the available attributes for a user account in Nubus for Kubernetes, you need to use the UDM HTTP REST API.
The access to the UDM HTTP REST API either requires that the API is reachable from outside the Kubernetes cluster, or that you have the proper permission to access the cluster through kubectl to temporarily open a port-forwarding. If you don’t have the proper permissions, ask your operator to provide the list of available account attributes by following the instructions.
For temporary access through port-forwarding, use the following steps:
Activate access to the UDM HTTP REST API from outside the Kubernetes cluster. See UDM HTTP REST API in Univention Nubus for Kubernetes - Nubus Customization and Modification Manual [4].
For temporary access, you can use port-forwarding from kubectl. To activate port-forwarding, use the commands in Listing 5.3. It provides access to the UDM HTTP REST API through your local port
8888. You don’t need to open access to the REST API from outside your cluster to lookup some values.$ export NAMESPACE_FOR_NUBUS="Set to your Kubernetes namespace" $ kubectl port-forward \ --namespace "$NAMESPACE_FOR_NUBUS" \ services/nubus-udm-rest-api \ 8888:9979
Open the interactive OpenAPI schema, see API location. Navigate to the section
users/user.If you use local port-forwarding, the URL is
http://localhost:8888/udm/schema/.For the available attributes, see the Schema of the
users/userproperties, in the POST request method. The Example Value listing shows the availablepropertieswith their key and value type.
5.3.3. Value syntax in a user account template#
If you use a user account template to create a user account,
the template overrides all attributes with the preset values of the template.
For an empty attribute in the user account template,
Nubus sets the attribute to the value "".
In a user account template, you can either define fixed values, for example for the address, or reference another attribute in the user management. User account templates support the following set of attribute value syntax:
<,>Use angle brackets
<,>to reference attributes or use syntax functions.<:lower>,<:upper>To convert attribute values to lowercase with
<:lower>or to uppercase with<:upper>.- Examples
Convert an attribute to lowercase:
<firstname:lower>.Convert the entire field to lowercase:
<lastname>@company.com<:lower>.
<:umlauts>To convert special characters, such as è, ä, or ß to corresponding ASCII characters, use
<:umlauts>.<:alphanum>To remove non-alphanumeric characters, such as
`(backtick) or#(hash), use<:alphanum>. If you apply the:alphanumfunction to the whole attribute, it removes all non-alphanumeric characters, even the@in email addresses. To avoid this behavior, only apply the function to attribute references or add the characters to the allow list.You can define an allow list of characters that
:alphanumignores through the UCR variabledirectory/manager/templates/alphanum/whitelist. The default value is"".To define an allow list of characters in Nubus for Kubernetes that
:alphanumignores, use the following steps:Add the
global.configUcr.directory.manager.templates.alphanum.whitelistHelm Chart variable to yourcustom_values.yamlvalues file and assign the characters.To activate your changes, update your Nubus installation through helm by following the steps in Apply configuration in Univention Nubus for Kubernetes - Operation Manual [1].
To apply the changes, you need to restart the UMC Server pod as described in Restart UMC Server pod in Univention Nubus for Kubernetes - Operation Manual [1].
<:strip>,<:trim>Remove all leading and trailing whitespace characters from the string.
- Sub-strings
Use square brackets
[,]to retrieve a sub-string of a value, or just one character. The index counting starts at0so that the index1corresponds to the second character of an attribute value. For example<firstname>[0],<firstname>[2:5].- Combine function
You can combine functions, for example
<:umlauts,upper>.
Important
The user account template allows substitutions for any value. However, there’s no syntax or semantics check. Empty attribute values return an empty string.
- Example
Assume the field definition
<firstname>.<lastname>@example.comfor an email address.If you use the user account template to create a user account and if you don’t specify a first name, the email address starts with a period and results in an invalid email address according to the email standard.
Similar sources of error are for example file paths. Nubus removes unresolvable attributes from a field, such as typing errors in the template.